All ISEE Upper Level Quantitative Resources
Example Questions
Example Question #1 :Data Analysis And Probability

Let the universal set
Examine the above Venn diagram. If each integer was to be placed in its correct region, which of the following would be placed in the gray area?
None of the other choices is correct.
None of the other choices is correct.
The grayed portion of the Venn diagram corresponds to those integers which are not in any of







All four choices have been eliminated.
Example Question #2 :Data Analysis And Probability

我n the above Venn diagram, the universal set is defined as
What is







Example Question #1 :How To Use A Venn Diagram
我n a school of



No answer is possible.
Based on the information given, you can construct the following Venn Diagram:

我n order to find the overlap, you need to find out how many are in the circles together. This is easy. Subtract:

Solving for
Example Question #1 :Data Analysis
我n a group of



No answer possible
Based on the information given, you can draw the following Venn Diagram:

To solve this, remember that the total number of values in the two circles is:
(We must do this because of the overlap. You need to subtract out one instance of that overlap.)
我f we assign the value
Example Question #5 :Data Analysis And Probability
我n a group of plants,


Based on the information, you can draw the following Venn Diagram:

我t is very easy to solve for the number of plants that have green leaves but not large ones. This is merely
Example Question #6 :Data Analysis And Probability
我n a group of



Cannot be determined
Based on the information given, you can draw the following Venn Diagram:

Now, you must begin by solving for






Now, we can find the number of people with只有书by subtracting


Example Question #7 :Data Analysis And Probability
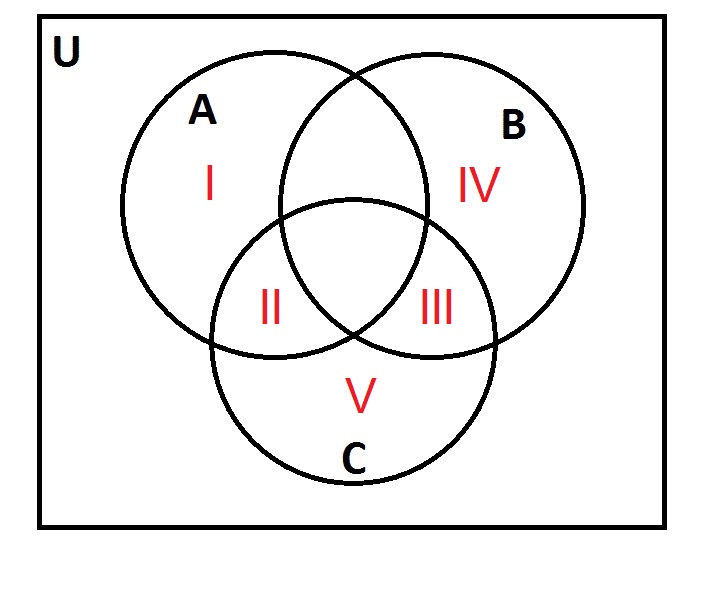
Examine the above Venn diagram. Let



James Abram Garfield was born in Ohio in 1831. In which region would he fall?
V
我V
我我
我我我
我
V
Carter would not fall in set A, since he was not a President born in Virginia.
He would not fall in B, since he was born before 1850.
He would fall in C, since his first name is James.
He would fall in the region included in set C, butnotA or B - this is Region V.
Example Question #8 :Data Analysis And Probability

Examine the above Venn diagram. Let



James Earl Carter was born in Georgia in 1924. In which region would he fall?
我
V
我我我
我V
我我
我我我
Carter would not fall in set A, since he was not a President born in Virginia.
He would fall in B, since he was born after 1850.
He would fall in C, since his first name is James.
He would fall in the region included in sets B and C, butnotA - this is Region III.
Example Question #1 :Venn Diagrams

Examine the above Venn diagram. Let universal set
Let


Which of the following would be a subset of the set represented by the shaded region in the diagram?
Note: for purposes of this question, "Y" is considered a consonant.
{usher, aspen, ester, order, earth}
{eagle, uvula, apnea, unsee, abide}
{potato, tomato, breeze, mimosa, magnolia}
{price, value, pinna, trove, three}
{catfish, division, rot, status, giving}
{price, value, pinna, trove, three}
The subset must comprise words that fall inside set


Therefore, all of the words in the subset must have exactly five letters, but cannot begin with a vowel or end with a consonant - that is, we are looking for a set of five-letter words that begin with a consonant and end with a vowel.
The only set among the five choices that matches this description is the set
{price, value, pinna, trove, three}.
Example Question #10 :Data Analysis And Probability

Examine the above Venn diagram. Let universal set
Let


Which of the following would be a subset of the set represented by the shaded region in the diagram?
Note: for purposes of this question, "Y" is considered a consonant.
{autism, enough, ideals, occult, unduly}
{tomato, potato, ravine, cabana, marine}
{plateau, portmanteau, calliope, marionette, taco}
{apnea, esoterica, irradiate, opulence, uvula}
{autistic, estrogen, ideology, opal, understand}
{plateau, portmanteau, calliope, marionette, taco}
The subset must comprise words that fall inside sets


Of the given choices, the only set whose elements fit this description is {plateau, portmanteau, calliope, marionette, taco}.
All ISEE Upper Level Quantitative Resources














































