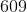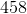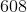All PSAT Math Resources
Example Questions
Example Question #1 :How To Find The Nth Term Of An Arithmetic Sequence
2, 8, 14, 20
The first term in the sequence is 2, and each following term is determined by adding 6. What is the value of the 50thterm?
3.02
3.20
3.00
296
296
We start by multiplying 6 times 46, since the first 4 terms are already listed. We then add the product, 276, to the last listed term, 20. This gives us our answer of 296.
Example Question #2 :How To Find The Nth Term Of An Arithmetic Sequence
Which of the following could not be a term in the sequence 5, 10, 15, 20...?
10005
3.5
2500
3.751
3.751
All answers in the sequence must end in a 5 or a 0.
Example Question #3 :How To Find The Nth Term Of An Arithmetic Sequence
In an arithmetic sequence, each term is two greater than the one that precedes it. If the sum of the first five terms of the sequence is equal to the difference between the first and fifth terms, what is the tenth term of the sequence?
10
–0.6
0.6
2.4
15.6
15.6
Let a1represent the first term of the sequence and anrepresent the nth term.
We are told that each term is two greater than the term that precedes it. Thus, we can say that:
a2= a1+ 2
a3.= a1+ 2 + 2 = a1+ 2(2)
a4= a1+ 3(2)
a5= a1+ 4(2)
an= a1+ (n-1)(2)
The problem tells us that the sum of the first five terms is equal to the difference between the fifth and first terms. Let's write an expression for the sum of the first five terms.
sum = a1+ (a1+ 2) + (a1+ 2(2)) +(一个1+ 3(2)) + (a1+ 4(2))
= 5a1+ 2 + 4 + 6 + 8
= 5a1+ 20
Next, we want to write an expression for the difference between the fifth and first terms.
a5- a1= a1+ 4(2) – a1= 8
Now, we set the two expressions equal and solve for a1.
5a1+ 20 = 8
Subtract 20 from both sides.
5a1= –12
a1= –2.4.
The question ultimately asks us for the tenth term of the sequence. Now, that we have the first term, we can find the tenth term.
a10= a1+ (10 – 1)(2)
a10= –2.4 + 9(2)
= 15.6
The answer is 15.6 .
Example Question #4 :How To Find The Nth Term Of An Arithmetic Sequence
In a certain sequence,an+1= (an)2– 1, whereanrepresents thenth term in the sequence. If the third term is equal to the square of the first term, and all of the terms are positive, then what is the value of (a2)(a3.)(a4)?
6
63
72
24
48
48
Leta1be the first term in the sequence. We can use the fact thatan+1= (an)2– 1 in order to find expressions for the second and third terms of the sequence in terms ofa1.
a2= (a1)2– 1
a3.= (a2)2– 1 = ((a1)2– 1)2– 1
We can use the fact that, in general, (a –b)2=a2– 2ab+b2in order to simplify the expression fora3..
a3.= ((a1)2– 1)2– 1
= (a1)4– 2(a1)2+ 1 – 1 = (a1)4– 2(a1)2
We are told that the third term is equal to the square of the first term.
a3.= (a1)2
We can substitute (a1)4– 2(a1)2fora3..
(a1)4– 2(a1)2= (a1)2
Subtract (a1)2from both sides.
(a1)4– 3(a1)2= 0
Factor out (a1)2from both terms.
(a1)2((a1)2– 3) = 0
This means that either (a1)2= 0, or (a1)2– 3 = 0.
If (a1)2= 0, thena1must be 0. However, we are told that all the terms of the sequence are positive. Therefore, the first term can't be 0.
Next, let's solve (a1)2– 3 = 0.
Add 3 to both sides.
(a1)2= 3
Take the square root of both sides.
a1= ±√3
However, since all the terms are positive, the only possible value fora1is √3.
Now, that we know thata1= √3, we can finda2,a3., anda4.
a2= (a1)2– 1 = (√3)2– 1 = 3 – 1 = 2
a3.= (a2)2– 1 = 22– 1 = 4 – 1 = 3
a4= (a3.)2– 1 = 32– 1 = 9 – 1 = 8
The question ultimately asks for the product of thea2,a3., anda4, which would be equal to 2(3)(8), or 48.
The answer is 48.
Example Question #1 :Nth Term Of An Arithmetic Sequence
In the given sequence, the first term is 3 and each term after is one less than three times the previous term.
What is the sixth term in the sequence?
The fourth term is: 3(23) – 1 = 69 – 1 = 68.
The fifth term is: 3(68) – 1 = 204 – 1 = 203.
The sixth term is: 3(203) – 1 = 609 – 1 = 608.
Example Question #6 :How To Find The Nth Term Of An Arithmetic Sequence
Consider the following sequence of numbers:
What will be the 8thterm in the sequence?
56
60
58
49
51
51
Each number in the sequence in 7 more than the number preceding it.
The equation for the terms in an arithmetic sequence is an= a1+ d (n - 1), where d is the difference.
The formula for the terms in this sequence is therefore an= 2 + 7(n-1).
Plug in 8 for n to find the 8thterm:
a8= 2 + 7(8-1) = 51
Example Question #1 :How To Find The Nth Term Of An Arithmetic Sequence
The second and fourth terms of an arithmetic sequence are 9 and 18, respectively. What is its first term?
The difference between the second and fourth terms of an arithmetic sequence is twice the common difference - or, equivalently, the common difference is half the difference between the second and fourth terms.
The common difference can be subtracted from the second term to obtain the first term:
Example Question #2 :How To Find The Nth Term Of An Arithmetic Sequence
A sequence of numbers is represented by the equation



Take the equation that represents the

The value of the 9th term is 747.
Example Question #1 :How To Find The Nth Term Of An Arithmetic Sequence
You are given a sequence with the same difference between consecutive terms. We know it starts at

From the given information, we know
Certified Tutor
All PSAT Math Resources