All AP Physics B Resources
Example Questions
Example Question #1 :Other Circular And Rotational Motion Concepts
A wheel of radius


Possible Answers:
有限公司rrect answer:
Explanation:
In order to find the distance the wheel travels, we need a way to convert angular displacement to linear displacement. We know that the circumference of a circle (or a wheel, in this case) is
Distance of one rotation equals: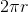
Since the wheel travels
Distance of
All AP Physics B Resources
Popular Subjects
SSAT Tutors in Washington DC,GMAT Tutors in Chicago,法国导师在丹佛,Spanish Tutors in Philadelphia,ISEE Tutors in Phoenix,GMAT Tutors in Washington DC,Physics Tutors in Dallas Fort Worth,Biology Tutors in Phoenix,有限公司mputer Science Tutors in Atlanta,GRE Tutors in Boston
Popular Courses & Classes
GMAT Courses & Classes in Miami,LSAT Courses & Classes in Miami,GMAT Courses & Classes in Washington DC,MCAT Courses & Classes in Houston,ACT Courses & Classes in Chicago,ISEE Courses & Classes in Chicago,GMAT Courses & Classes in Denver,GRE Courses & Classes in Dallas Fort Worth,SAT Courses & Classes in New York City,GMAT Courses & Classes in Seattle